Health Writer | Posted on |
All you need to know about prostate cancer
0
1896 Views
The prostate is a walnut-sized organ. Located just below the bladder, in front of the rectum, is a function is the production of semen.
Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate gland multiply abnormally, without control, forming a mass or a tumour in the prostate gland.
If you are suffering from prostate cancer, it is important to know about the disease in detail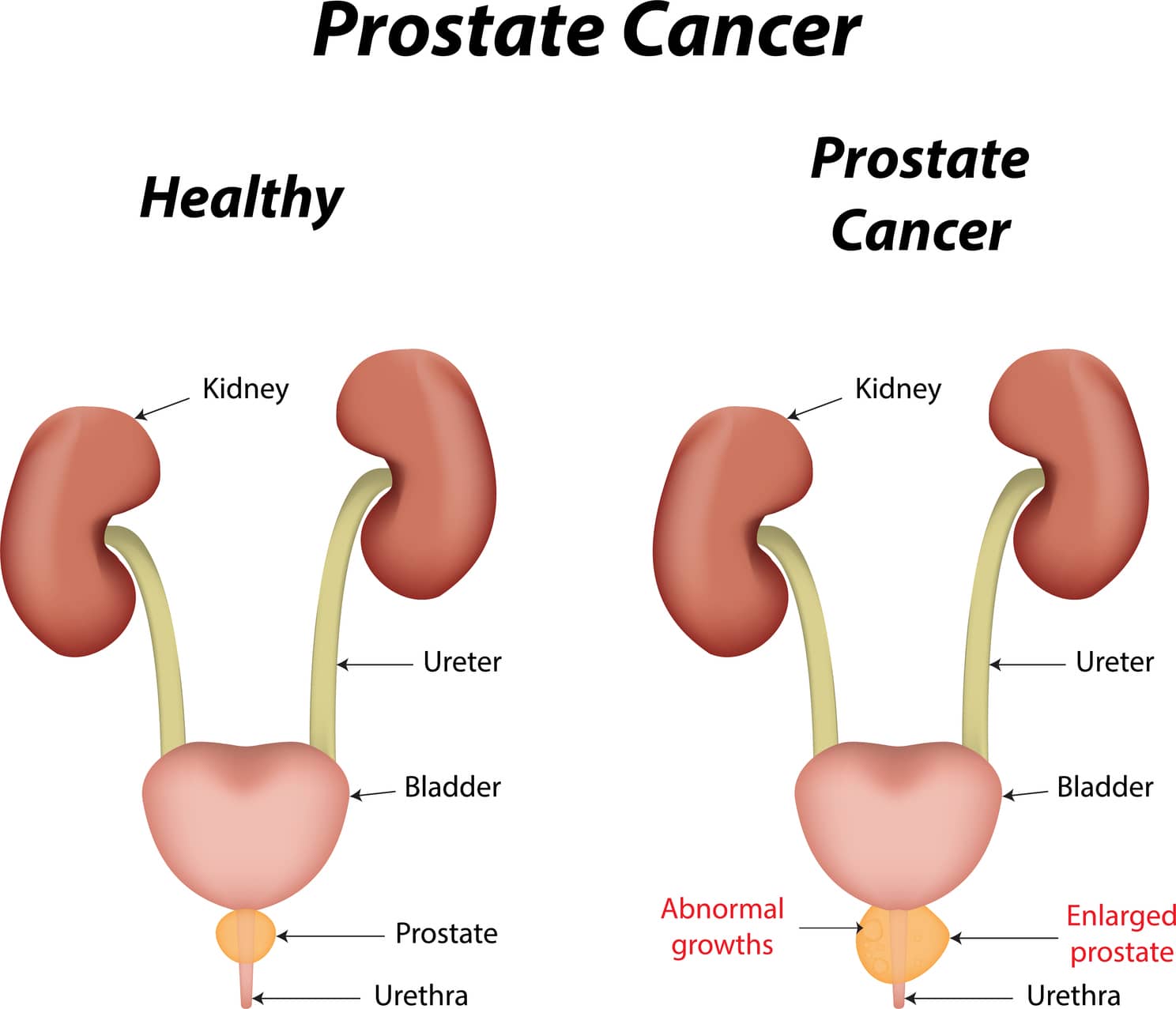
Risk Factors, Signs and Symptoms
Risk Factors
There are numerous factors that can increase your risk of developing prostate cancer. Talk to your physician if you believe you may be at risk for developing prostate cancer.
Common risk factors include:
• Age - Most men diagnosed with prostate cancer are over 65 years of age.
• Family History- The likelihood of getting prostate cancer is increased if your father, brother or son had prostate cancer.
• Race - Prostate cancer is more common among black men than white.
• Alterations in Prostate - Men with high-grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia (PIN), an abnormal cell condition, may be at higher risk of developing prostate cancer.
• Diet high in processed meat, red meat, milk products or low in certain vegetables.
Diagnosis and Staging
In order to diagnose prostate cancer, your physician will perform a physical exam, and may tell you to perform some additional tests including one or more of the following:
• Transrectal ultrasound -The probe used in this technique makes use of sound waves to check for abnormal growth in the prostate.
• Biopsy - Small tissue samples are removed from the prostate. These samples are observed under a microscope to check for cancer cells.
• Digital rectal exam (DRE) - This test checks if a man has symptoms of an enlarged prostate.
• Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test - This blood test checks levels of PSA (prostate-specific antigen) in the blood. High levels of PSA often indicate the presence of prostate cancer.
• Imaging scans – Scanning techniques such as a bone scan, ultrasound, CT scan or MRI are used to determine if cancer has spread to the other organs. There is also a new technique known as PET scan that is sometimes used.
Treatment
Treatment for prostate cancer depends on the stage of cancer, the grade of the tumour, the age of the person, the number of biopsy samples that indicate the presence of cancer cells, and the person’s overall health condition. You should always talk to your doctor about treatment options before starting the treatment.
Treatment options include:
• Surgery
• Radiation Therapy
• Hormone Therapy
• Chemotherapy
• Immunotherapy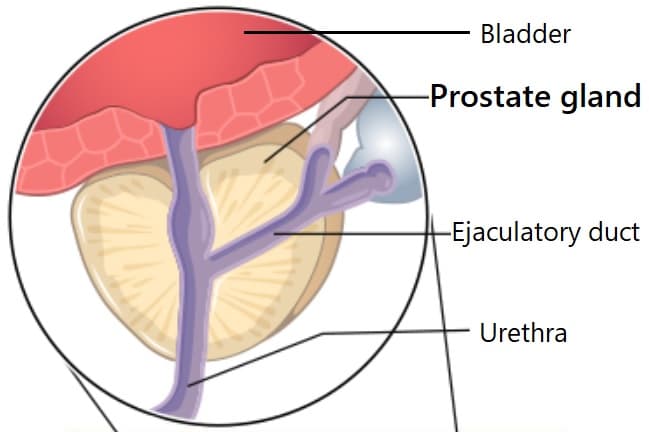
Side Effects Management
Everyone reacts differently to cancer treatment and experience different side effects. Always inform your doctor if you are experiencing any problem such as erectile dysfunction, pain, nausea, fatigue, incontinence and bodily changes that affect your self-esteem. These things are common and can be managed successfully.
Recovery after prostate cancer depends on the type of treatment, stage of cancer and other factors. Follow-up is extremely important in case of any type of cancer.
