Table of Contents
- Understanding the Chrome “Not Secure” Warning
- Common Causes of the “Not Secure” Warning
- How SSL and HTTPS Work
- Impact of the “Not Secure” Warning
- How to Check Your Website for Security Issues
- How to Fix the Chrome “Not Secure” Warning
- Step-by-Step Fixes by Website Type
- Preventing the “Not Secure” Warning in the Future
- Best Practices for Website Security
- Conclusion
Understanding the Chrome “Not Secure” Warning
In today's era, we have various Search Engines to answer our query. One such is Chrome. Around 3.62 to 3.8 billion people around the world use it which increases its responsibility to keep people browsing risk free. One way to do this is by popping up “Not Secure” warning.
What Does “Not Secure” Mean in Chrome?
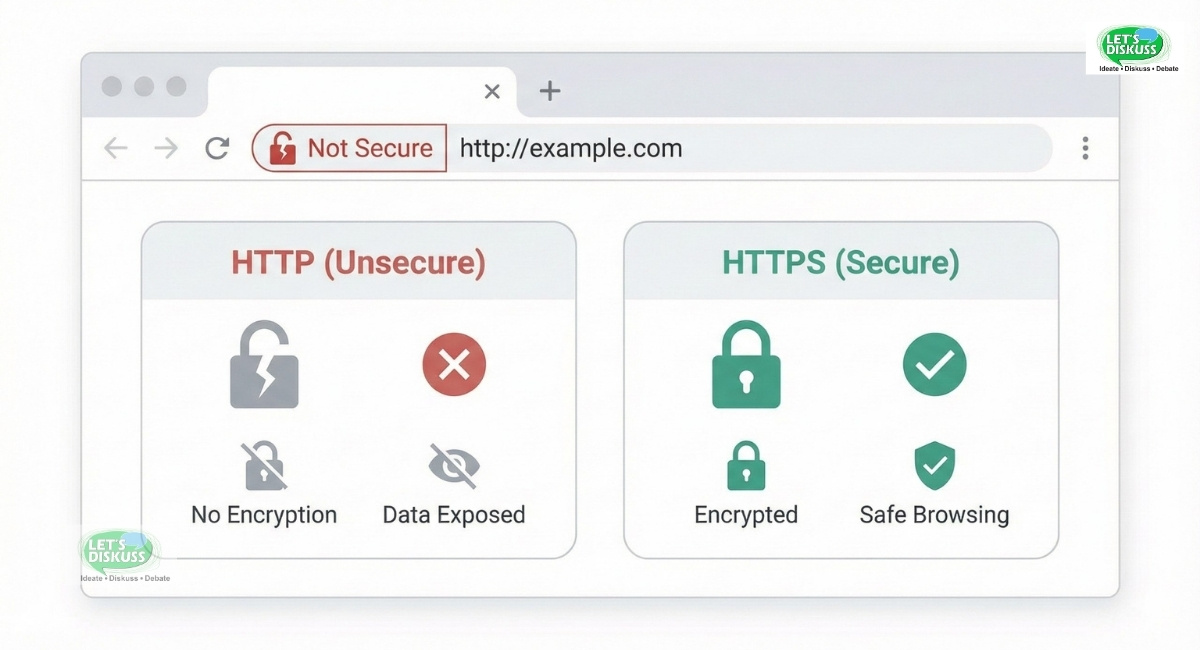
When Chrome shows “Not Secure” on any website you open, it means that the website is not secured and your data ( personal information like name, date of birth, password) is flowing in plain text rather than codes.
When and Why the Warning Appears
The Chrome “Not Secure” Warning pops up when a user visits a website, enters their personal information, or shares their passwords. It appears to alert the user that the website is not encrypted and risky.
Evolution of Chrome Security Warnings
Throughout the years, Chrome Security Warnings has evolved due to risk of missing data by third-party and cybersecurity reasons.
- Till 2017, Chrome used to provide Safe Browsing to save users from browsing phishing sites.
- During 2018, chrome started putting “Not Secure” in the address bar to alert users and remove all signs of safe browsing so that users leave, avoid, or bounce from the website.
- In 2020, Chrome introduced “Enhanced Safe Browsing” to detect “Not Secure” Websites and uses ML Driven protection to alert the user on a real-time basis.
- During 2022, Chrome introduced the websites with “Always use Secure Connections” which says about HTTPS first to understand the users.
- Recently, in 2026, Chrome has made it mandatory for all websites to become HTTPS and warns the users so as to create an overall secured web browsing experience for users.
How Browsers Detect Website Security
Web Browsers evaluate how data and information is interexchanging between website server and user's browser. They look for an encrypted connection to provide a safe and risk free experience to users and alert them immediately in case of a “HTTP” or Misconfigured Website.
A “HTTPS” Encryption led to security of data by processing information in codes rather than plain text.
The web browser like chrome does it by checking for SSL/TLS Certificate. They check for if the certificate is not present, unauthorised or issued by a misleading party.
Common Causes of the “Not Secure” Warning
The “Not Secure” Warning comes due to the mission of encrypted flow of information. Below are some common causes of “Not Secure” warnings. A Website owner must fix these issues to prevent their website getting blacklisted on browsers.
Missing SSL Certificate
One of the foremost causes is missing SSL Certificates. If a website has an SSLCertificate missing, or it has expired, or issued by an unauthorised entity, then the website runs on HTTP instead of HTTPS. This leads to marking the website as “Not Secure” for users.
Expired or Invalid SSL Certificate
Only a single time renewal won't work. Website Owners need to continuously renew their SSL Certificate to save their website from getting flagged as “Not Secure”. Expired or Invalid SSL Certificate lead web browsers to put it as a not secured website.
Mixed Content Issues (HTTP & HTTPS)
Mixed Content issues emerge when some part of a website is running over HTTPS but other content like images, videos, or scripts loads on HTTP. This needs to fixchrome security warning to not mark the website as “Not Secure” as some resources are still not encrypted.
Incorrect SSL Installation
Another common cause that generally emerged is incorrect SSL Installation. This means incorrect domain mapping, improper server configuration, or missing intermediate certificates.
Outdated Security Protocol
Browsers like chrome are continuously evolving and changing their methods to protect user's data. If any website is still following outdated security protocol, the browser automatically rejects them and flags them as “Not Secure”.
How SSL and HTTPS Work
For a web safe browsing experience, the website loads on HTTPS and issues SSL Certificate which are viral for ensuring privacy and trust between website and user.
What Is SSL/TLS?
SSL (Secure Socket Layers) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are security protocols followed by website owners to ensure users that their data and information is safe and not transferable to any third-party users. They use encryption technologies to establish a secure connection when an exchange of data like credentials and personal information is shared between a website and a user.
HTTPS vs HTTP Security Explained
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is a standard protocol that implies transfer of data and information from a user to a website but does not ensure security which means data can be altered or tempered.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is the extended version of HTTP but with encrypted security. HTTPS requires SSL/TLS Certificate to form a safe and risk free interaction and data security of users which they share with the website.
Encryption, Authentication, and Data Integrity
Encryption is transmission of data into secured codes so that only the shared parties have access to them which is regulated through SSL/TLS Certificate. Encryption prevents third-party access of data.
Authentication can be understood as checking the domain mapping and identity of the website to legitimate the website and inform the users about it.
Data Integrity refers to securing data to not get altered and misconfigured. In case of tempering or altering, data can be misused and goes against the users.
Role of Certificate Authorities
Certificate Authorities main role is to validate the identity and legitimacy of a website. Certificate Authorities check for the organisation behind the website and look for SSL/TLS Certificates.
Web Browsers have a list of recognised certificate authorities which they check for websites active on the browser and flagged “Not Secure” to websites that do not have certificates from their list of recognised authorities.
Impact of the “Not Secure” Warning
“Not Secure” Warning on a website can lead to major impacts for website owners. Below are some of the major consequences:
Loss of User Trust
When a user lands on a website and it is flagged as “Not Secure” can lead to loss of user trust on the website. This can highly impact the reach and visibility of the website.
Higher Bounce Rates
A “Not Secure” pop-up can lead to higher bounce rates with users immediately leaving the website. This can lead to impact on revenue and temper the reputation of the organization.
SEO and Search Ranking Impact
Ranking on search engines is a must factor for increased visibility and reach that can hamper with a “Not Secure” warning on any website. It will impact Search Ranking and can even completely make the website invisible.
Effects on Conversions and Sales
When users bounce from a website due to “Not Secure” warning, it automatically leads to impact conversion and sales as people’s trust will be gone and reputation will be tarnished.
Brand Reputation Damage
Overall, a “Not Secure” warning leads to damage to brand reputation and a negative perception. Repeated warnings make the users not interested in the brand even after following security protocols.
It's best to check for renewal of certificates or any protocol related to security and transfer of data to provide a safe browsing experience to the users.
How to Check Your Website for Security Issues
Security based consequences can lead to a major impact on a website's visibility and search engine rankings which makes it essential to check your website regularly for security issues. Today, we have browsers and tools that facilitate security issues discovery and solutions.
Using Chrome DevTools
Chrome DevTools is an in-built feature available to website owners and developers to check for security issues regularly and fix them. It's present in Google Chrome and led website owners to handle misconfigured information or security status.
SSL Certificate Testing Tools
Website owners can use various SSL Certificate testing tools available on the internet. These testing tools can provide information about the validity, authority, and expiration of these certificates.
Using these testing tools helps website owners to prevent security consequences and upgrade their renewal regularly.
Identifying Mixed Content Errors
Mixed Content Errors comes when some part of website like images, videos or scripts loads on HTTP and the website itself is running over HTTPS. It can still lead to security and identity issues.
Using browser developer tools and security reports can help website owners to mixed content error fix.
Monitoring Website Security Regularly
Evolving protocols and malware detection softwares can pop up a “Not Secure” warning to your website. Hence, routine checks and reminders are essential to stay up to date and follow all the required protocols. This will lead to increased search engine rankings and improved brand image.
How to Fix “Not Secure” Warning
Generally, the “Not Secure” warning can be fixed by understanding security reasons. The most common way is to check for renewal of SSL Certificate.
Installing an SSL Certificate
Installing a SSL Certificate is the first step to secure your website. SSL Certificate led the website to run on HTTPS which makes it a safe and secure website.
Renewing or Replacing an SSL Certificate
Mere installation of a SSL Certificate is not enough. Timely renewal or replacing of SSL certificate is essential as SSL Certificate gets invalid or expires over the time.
Fixing Mixed Content Errors
Mixed Content Errors issues emerge when some part of a website like images, videos or scripts loads over HTTP. Fixing it requires each content to load over HTTPS so that it doesn't cause any security issues.
Redirecting HTTP to HTTPS
Website owners redirect content running over HTTP to HTTPS so that users can load different content of websites without risk or harm. This involves removing all content running over unsecured sites and providing a safe browsing experience to users.
Updating Website URLs and Resources
After redirecting, updating website URLs is the next step. Check for internal links, embedded resources and backlinks URLs and update them based on the latest security protocols.
Step-by-Step Fixes by Website Type
Website owners have different website types and based on that “step-by-step” fixes have to be taken. However, Installing a SSL Certificate and running over HTTPS is basically for all.
Fixing “Not Secure” on WordPress Sites
For WordPress Sites, installing a SSL certificate or mixed Content Errors remain the key to fix the “Not Secure” pop-up.
You can fix it through installing a SSL certificate on your website and apply it on a hosting service provider.
By updating the settings on WordPress sites and loading HTTP to HTTPS.
Using SSL plugins and security reports to check for any emerging issues.
Fixing Issues on E-Commerce Websites
Fixing issues on e-commerce websites is crucial for owners as these websites handle payment gateway, password protection and login credentials which are sensitive data.
You can be fixed it through:
Installing a SSL Certificate that covers every content on the website.
Loading data from HTTP to HTTPS to secure the access.
Check for proper domain mapping across all gateways like payment gateway, order processing, and invoicing.
Fixes for Static HTML Websites
Static HTML Websites need to be manually updated over time.
You can fix it by:
Installing a SSL Certificate on the website.
Redirect website to load over HTTPS from HTTP.
Updating internal links, embedded resources and external references.
Fixing mixed Content Errors and run them on HTTPS.
Hosting Provider-Specific Solutions
Website owners can also opt for hosting provider-specific solutions.
Hosting-providers themselves provide in-built features like SSL certificate installation, redirecting HTTP to HTTPS, certificate renewal on expiry, and tools to update content URLs.
Preventing the “Not Secure” Warning in the Future
Auto-Renewing SSL Certificates
Website owners can opt for auto-renewal of SSL certificate through hosting provider or from a recognised certificate authorities.
Enabling HSTS
HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security) is a policy that helps browsers to stay connected to websites directed to HTTPS. This can enable a safe and secure browsing experience for users.
Regular Security Audits
Regular Security Audits can help in finding potential issues and the website owners can solve them beforehand. This can involve renewal of SSL Certificate or checking security reports along with reviewing server settings.
Keeping CMS, Plugins, and Servers Updated
Content Management Systems, SSL Plugins and Servers need to be regularly updated so as to decrease the chances of mixed content errors or degraded encryption.
Best Practices for Website Security
Website security is a must to protect user's data, increase search rankings, and improve visibility. Along with SSL plugins and loading on HTTPS, there are more ways to secure your website and facilitate secure and safe browsing.
Secure Forms and User Data
Forms that collect information like name, email, passwords, etc. should be highly secured and encrypted to protect user data. Encryption will create data inaccessible to third-party members.
Strong Authentication Methods
Strong Authentication Methods include some practices that protects a user from transfer of his sensitive data through applying methods like using a personalized strong password, multi-factor authorisation and limited login attempts. These methods can save the data and make it non-accessible to cybersecurity risk.
Backup and Recovery Planning
Backup plans must be planned in advance to schedule automatic and routine backups. These backups help in case of data loss or cyberattack.
Similarly, Recovery planning should be planned to protect user data and store critical information in a secured space.
Combining SSL with Other Security Tools
Mere installation of SSL certificate won't be enough for securing your site. Combining it with other security tools will create an additional layer of protection and result in safe browsing.
These tools can be firewalls, malware detection, intrusion detection systems. Using these tools strengthens a website's security and keeps it risk-free.
Conclusion
Why Website Security Is No Longer Optional
People's reliance on search engines has been expanding more. And in the upcoming time, it will only expand. Hence, providing safe and secure browsing is now no longer optional but mandatory. In case of failure to do so, website owners can face several consequences like damaged reputation, blacklisting, loss of people's trust, and cyber attacks.
User's data is a critical and sensitive case and keeping that in mind several security measures should be taken. From installing a SSL certificate to security reports to HTTPS protocol, website owners must regulate and automate check-ups and update their website based on the latest chrome “Not Secure” warning policy.
Creating a Safe and Trustworthy Browsing Experience
Creating a safe and trustworthy browsing experience is the key to sustain and maintain your presence in web browsers. Web Browsers are continuously updating and taking measures to protect user data. Likewise, website owners must keep checking their websites for any security upgrade like renewal of SSL certificate.
With increasing technologies, cyberattack has become the increased risk of sharing sensitive data. Hence, it's mandatory to secure your website to avoid data breaches or misplacing critical user data.
FAQs
- What does “Not Secure” mean in Chrome?
The “Not Secure” Warning in Chrome means that the website is not secured and any shared data and information can be transferred to third-party. It happens mainly due to missing SSL certificate.
- Why does my website show “Not Secure” in Chrome?
Your Website is showing “Not Secure” in Chrome due to absence of SSL certificate or an expired or authorised SSL certificate due to which website is loading on HTTP instead of HTTPS.
- How do I fix the Chrome “Not Secure” warning?
You can fix chrome “Not Secure” warning through installing a SSL certification and fixing mixed content error issues.
- Does “Not Secure” affect SEO?
Yes. “Not Secure” warning affect SEO as users avoid these websites which leads to low visibility and therefore affect overall search engine rankings.
- Is a free SSL certificate enough?
In the majority of cases, a free SSL certificate is enough. However, if you run an e-commerce website or financial website and need large critical user data, then you must opt for a paid SSL certificate.
- What is mixed content and how do I fix it?
Mixed Content is when some part of your website like images, videos or scripts loads on HTTP instead HTTPS. You can fix it by running all your website information at HTTPS.
- Why does Chrome still show “Not Secure” after installing SSL?
Chrome can still show “Not Secure” warning due to non-renewal of SSL Certificate or in case it is from an unrecognised certificate authorities.
- Will visitors see warnings if my site is “Not Secure”?
Yes. Visitors will be alerted by chrome during your site visit if browsers find it “Not Secure”.
- Do all websites need HTTPS?
Yes. All websites need HTTPS. It doesn't whether the website is a WordPress site or a static HTML site. Every website must have HTTPS. - How long does it take to remove the “Not Secure” warning?
In most cases, the warning disappears immediately or within a few hours after SSL installation and proper configuration. However, delays may occur due to browser caching, DNS propagation, or unresolved mixed content issues.

